A conductive material made from aluminum, used to distribute electricity within electrical panels or systems. They provide a low-resistance path for electrical current and are commonly used in substations and switchgear.
aluminum busbar Supplied Forms
-
1050 aluminum flat bar busbar
1050 aluminum busbars (aluminum flat bars) are a type of high-purity aluminum alloy, typically containing at least 99.5% aluminum, classified as EC-grade aluminum (electrical conductivity grade aluminum).
-
1060 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
The 1060 aluminum busbar is a conductive busbar made primarily of 1060 aluminum alloy, commonly used in power systems and electrical equipment.
-
1070 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
The 1070 electrical aluminum busbar, with its excellent conductivity, lightweight, and corrosion resistance, has become an important component in power transmission and distribution systems, suitable for various electrical equipment and applications.
-
1350 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
1350 electrical aluminum busbar is a widely used aluminum alloy conductor in electrical engineering and distribution systems, featuring excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical properties.
-
6061 T4 T6 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
The 6061 aluminum busbar is a special type of electrical busbar made from 6061 aluminum alloy. Due to its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, it is widely used in electrical and structural applications.
-
6063 T4 T6 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
6063 aluminum busbars are electrical conductors made from 6063 aluminum alloy. Due to their lightweight and ability to effectively handle large currents, they are commonly used in power distribution systems.
-
6101 T6 T61 T64 Electrical Aluminum Busbar
6101 aluminum busbars are available in various specifications, including different cross-sectional shapes (such as rectangular, round, etc.) and sizes, to meet specific current-carrying capacities and installation requirements.
-
Tin-plated Aluminum Bus Bar
High quality tin-plated aluminum busbars are ideal for power generation, telecommunications, electric vehicles and transportation systems. Available in custom sizes and conforms to ASTM B545 standards.
-
Copper Clad Aluminum Busbar
Copper Clad Aluminum Busbar combines the high conductivity of copper with the lightweight advantages of aluminum, providing efficient and stable power transmission solutions for power distribution systems and other fields, reducing costs and weight.
-
Nickel-plated aluminum busbar
Nickel-plated aluminum busbars combine high conductivity, lightweight properties, and enhanced durability, making them the preferred choice for various electrical applications.
-
Flexible Aluminum Busbar
Flexible aluminum busbars can be bent and formed to fit a variety of configurations, making them ideal for installation in tight or complex spaces.
-
Aluminum Tubular Busbar
Aluminum tubular busbars are the ideal solution for modern electrical applications. Designed for efficiency and high performance, these busbars ensure stable power transmission while reducing weight and optimizing space in your system.
Aluminum busbars are metal strips or rods used for power distribution, conducting large currents in switchgear, substations, distribution boards, or industrial equipment. They act as central hubs that connect multiple circuits, ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission.
Aluminum busbars are used in electrical systems to achieve efficient conduction and distribution of power. These busbars are typically made from high-purity aluminum alloys, serving as central connection points that allow power to be collected from the input source and distributed to multiple circuits. Their design and material properties make them essential components in various electrical applications.

HC Aluminum - High-Quality Aluminum Busbar Supplier
HC Aluminum offers a comprehensive range of electrical busbar products, including aluminum busbars, copper busbars, and copper-clad aluminum busbars. Popular aluminum busbar products include 6101, 1060, 1100, 1350, 6061, 6063, etc., with a full range of specifications and competitive prices.
In addition to standard products, we can provide customized solutions for specialized applications within a short lead time.
- Shape: Flat, angled, or custom-extruded profiles.
- Surface treatment: Anodizing, plating, spraying, etc.; typically aluminum plated with silver, tin, or nickel.
Aluminum Busbar Standards and Compliance
- Main standards: IEC 61439, ANSI C37.20, ASTM B317 (material specifications).
- Testing: Temperature rise, short-circuit withstand, HIPOT testing, and corrosion resistance (e.g., salt spray test).
Aluminum Busbar Material Properties
- Conductivity: The electrical conductivity of aluminum is about 61% of that of copper (37.7 MS/m vs. 58.0 MS/m). To match the current carrying capacity of copper, aluminum busbars need approximately 56% larger cross-sectional area.
- Weight: With a density of 2.7 g/cm³ (compared to copper at 8.96 g/cm³), aluminum busbars are approximately 50-60% lighter for the same current capacity.
- Corrosion resistance: Forms a protective oxide layer; optional coatings (anodizing, tin-plating/silver-plating) enhance durability.
- Non-magnetic: Ideal for applications requiring minimal electromagnetic interference.
- Thermal expansion: Higher than copper; design adjustments may be required to prevent mechanical stress.
Aluminum Busbar Design Considerations
- Shape: Rectangular (most common for high surface area), round, or tubular (used to mitigate skin effect in high-frequency applications).
- Rated current: Determined by the cross-sectional area, ambient temperature, and cooling conditions (e.g., a 100mm x 10mm rectangular busbar can carry ~1200A in a 35°C environment).
- Temperature rise: Must comply with standards (e.g., IEC 61439) to prevent overheating. Aluminum has lower thermal conductivity than copper. To compensate for heat dissipation, we generally recommend increasing the surface area to improve heat exchange and enhance cooling efficiency.
- Mechanical strength: The softness of aluminum may require thicker profiles or additional support to prevent sagging.
- Surface treatment: Polishing, anodizing, or plating (tin/silver) to reduce oxidation and improve contact resistance.
Aluminum Busbar Features
- Conductivity: Aluminum offers excellent conductivity, about 61% of copper’s, allowing for efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is much lighter than copper, making aluminum busbars easier to handle and install. The reduced weight can save on transportation and installation costs.
- Corrosion resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, offering corrosion resistance and enhancing the durability of the busbar, especially in outdoor or harsh environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Generally, aluminum is more affordable than copper, making aluminum busbars a cost-effective choice for many applications.

Aluminum Busbar Applications
- Power distribution: Aluminum busbars are widely used in power distribution systems, including substations and distribution boards, to efficiently distribute power to various circuits.
- Switchgear and control panels: They are essential components in switchgear and control panels, helping to safely and efficiently distribute power.
- Renewable energy systems: Aluminum busbars are used in renewable energy installations, such as solar systems, to connect and distribute power from solar panels to inverters and other components.
- Power distribution in substations, data centers, and industrial plants.
- Electric vehicles (battery interconnections).
- Busbar trunking systems in commercial buildings.
Advantages of Aluminum Busbars over Copper
- Advantages: Lower cost (saving 30-50%), lighter weight, corrosion-resistant, recyclable.
- Disadvantages: Larger size, lower conductivity, possible oxidation at joints.
Copper and Aluminum Current Carrying Capacity Comparison Table
| Ampacity Conversion Chart | Copper C110 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | Aluminum 6101 | 30° C Rise | 50° C Rise | 65° C Rise | ||||
| Flat Bar Size in Inches | Sq. In | Circ Mils Thousands | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp* | Weight Per Ft in Lb. | DC Resistance at 20° C, Microhms/Ft | 60 Hz Ampacity Amp** | ||||
| 1/16 x 1/2 | 0.0312 | 39.7 | 0.121 | 264 | 103 | 136 | 157 | 0.037 | 494 | 58 | 76 | 88 |
| 1/16 x 3/4 | 0.0469 | 59.7 | 0.181 | 175 | 145 | 193 | 225 | 0.055 | 327 | 81 | 108 | 126 |
| 1/16 x 1 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.242 | 132 | 187 | 250 | 285 | 0.073 | 247 | 105 | 140 | 160 |
| 1/16 x 1 1/2 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 270 | 355 | 410 | 0.110 | 164 | 151 | 199 | 230 |
| 1/16 x 2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 345 | 460 | 530 | 0.146 | 123 | 193 | 258 | 297 |
| 1/8 x 1/2 | 0.0625 | 79.6 | 0.241 | 132 | 153 | 205 | 235 | 0.073 | 247 | 86 | 115 | 132 |
| 1/8 x 3/4 | 0.0938 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 215 | 285 | 325 | 0.110 | 164 | 120 | 160 | 182 |
| 1/8 x 1 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 270 | 360 | 415 | 0.146 | 123 | 151 | 202 | 232 |
| 1/8 x 1 1/2 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 385 | 510 | 590 | 0.220 | 82 | 216 | 286 | 330 |
| 1/8 x 2 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 495 | 660 | 760 | 0.293 | 62 | 277 | 370 | 426 |
| 1/8 x 2 1/2 | 0.312 | 397 | 1.210 | 26.4 | 600 | 800 | 920 | 0.365 | 49 | 336 | 448 | 515 |
| 1/8 x 3 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.439 | 41 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/8 x 3 1/2 | 0.438 | 558 | 1.690 | 18.8 | 810 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.512 | 35 | 454 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/8 x 4 | 0.5 | 636 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 900 | 1200 | 1400 | 0.585 | 31 | 504 | 672 | 784 |
| 3/16 x 1/2 | 0.09375 | 119 | 0.362 | 87.7 | 195 | 260 | 300 | 0.110 | 164 | 109 | 146 | 168 |
| 3/16 x 3/4 | 0.141 | 179 | 0.545 | 58.4 | 270 | 360 | 415 | 0.165 | 109 | 151 | 202 | 232 |
| 3/16 x 1 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 340 | 455 | 520 | 0.220 | 82 | 190 | 255 | 291 |
| 3/16 x 1 1/2 | 0.281 | 358 | 1.090 | 29.3 | 480 | 630 | 730 | 0.329 | 55 | 269 | 353 | 409 |
| 3/16 x 2 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 610 | 810 | 940 | 0.439 | 41 | 342 | 454 | 526 |
| 3/16 x 2 1/2 | 0.469 | 597 | 1.810 | 17.5 | 740 | 980 | 1150 | 0.549 | 33 | 414 | 549 | 644 |
| 3/16 x 3 | 0.562 | 715 | 2.170 | 14.6 | 870 | 1150 | 1350 | 0.658 | 27 | 487 | 644 | 756 |
| 3/16 x 3 1/2 | 0.656 | 835 | 2.530 | 12.5 | 990 | 1300 | 1500 | 0.768 | 23 | 554 | 728 | 840 |
| 3/16 x 4 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.900 | 11 | 1100 | 1450 | 1700 | 0.878 | 21 | 616 | 812 | 952 |
| 1/4 x 1/2 | 0.125 | 159 | 0.483 | 65.8 | 240 | 315 | 360 | 0.146 | 123 | 134 | 176 | 202 |
| 1/4 x 3/4 | 0.188 | 239 | 0.726 | 43.8 | 320 | 425 | 490 | 0.220 | 82 | 179 | 238 | 274 |
| 1/4 x 1 | 0.25 | 318 | 0.966 | 32.9 | 400 | 530 | 620 | 0.293 | 62 | 224 | 297 | 347 |
| 1/4 x 1 1/2 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 560 | 740 | 880 | 0.439 | 41 | 314 | 414 | 482 |
| 1/4 x 2 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.930 | 16.5 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.585 | 31 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 1/4 x 2 1/2 | 0.625 | 796 | 2.410 | 13.2 | 850 | 1150 | 1300 | 0.731 | 25 | 476 | 644 | 728 |
| 1/4 x 3 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.900 | 11 | 990 | 1300 | 1550 | 0.878 | 21 | 554 | 728 | 868 |
| 1/4 x 3 1/2 | 0.875 | 1110 | 3.380 | 9.4 | 1150 | 1500 | 1750 | 1.024 | 18 | 644 | 840 | 980 |
| 1/4 x 4 | 1 | 1270 | 3.860 | 8.23 | 1250 | 1700 | 1950 | 1.170 | 15 | 700 | 952 | 1092 |
| 1/4 x 5 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.830 | 6.58 | 1500 | 2000 | 2350 | 1.463 | 12 | 840 | 1120 | 1316 |
| 1/4 x 6 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.800 | 5.49 | 1750 | 2350 | 2700 | 1.755 | 10 | 980 | 1316 | 1512 |
| 3/8 x 3/4 | 0.281 | 368 | 1.090 | 29.3 | 415 | 550 | 630 | 0.329 | 55 | 232 | 308 | 353 |
| 3/8 x 1 | 0.375 | 477 | 1.450 | 21.9 | 510 | 680 | 790 | 0.439 | 41 | 286 | 381 | 442 |
| 3/8 x 1 1/2 | 0.562 | 715 | 2.170 | 14.6 | 710 | 940 | 1100 | 0.658 | 27 | 398 | 526 | 616 |
| 3/8 x 2 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.900 | 11 | 880 | 1150 | 1350 | 0.878 | 21 | 493 | 644 | 756 |
| 3/8 x 2 1/2 | 0.938 | 1190 | 3.620 | 8.77 | 1050 | 1400 | 1600 | 1.097 | 16 | 5.88 | 784 | 896 |
| 3/8 x 3 | 1.12 | 1430 | 4.350 | 7.35 | 1200 | 1600 | 1850 | 1.310 | 14 | 672 | 896 | 1036 |
| 3/8 x 3 1/2 | 1.31 | 1670 | 5.060 | 6.38 | 1350 | 1800 | 2100 | 1.533 | 12 | 756 | 1008 | 1176 |
| 3/8 x 4 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.8 | 5.49 | 1500 | 2000 | 2350 | 1.755 | 10 | 840 | 1120 | 1316 |
| 3/8 x 5 | 1.88 | 2390 | 7.26 | 4.38 | 1800 | 2400 | 2800 | 2.2 | 8 | 1008 | 1344 | 1568 |
| 3/8 x 6 | 2.25 | 2860 | 8.69 | 3.66 | 2100 | 2800 | 3250 | 2.633 | 7 | 1176 | 1568 | 1820 |
| 1/2 x 1 | 0.5 | 637 | 1.93 | 16.5 | 620 | 820 | 940 | 0.585 | 31 | 347 | 459 | 526 |
| 1/2 x 1 1/2 | 0.75 | 955 | 2.9 | 11 | 830 | 1100 | 1250 | 0.878 | 21 | 465 | 616 | 700 |
| 1/2 x 2 | 1 | 1270 | 3.86 | 8.23 | 1000 | 1350 | 1550 | 1.17 | 15 | 560 | 756 | 868 |
| 1/2 x 2 1/2 | 1.25 | 1590 | 4.83 | 6.58 | 1200 | 1600 | 1850 | 1.463 | 12 | 672 | 896 | 1036 |
| 1/2 x 3 | 1.5 | 1910 | 5.8 | 5.49 | 1400 | 1850 | 2150 | 1.755 | 10 | 784 | 1036 | 1204 |
| 1/2 x 3 1/2 | 1.75 | 2230 | 6.76 | 4.7 | 1550 | 2100 | 2400 | 2.048 | 9 | 868 | 1176 | 1344 |
| 1/2 x 4 | 2 | 2550 | 7.73 | 4.11 | 1700 | 2300 | 2650 | 2.34 | 8 | 952 | 1288 | 1484 |
| 1/2 x 5 | 2.5 | 3180 | 9.66 | 3.29 | 2050 | 2750 | 3150 | 2.925 | 6 | 1148 | 1540 | 1764 |
| 1/2 x 6 | 3 | 3820 | 11.6 | 2.74 | 2400 | 3150 | 3650 | 3.51 | 5 | 1344 | 1764 | 2044 |
| 1/2 x 8 | 4 | 5090 | 15.5 | 2.06 | 3000 | 4000 | 4600 | 4.68 | 4 | 1680 | 2240 | 2576 |
- **Source: Copper Development Organization https://www.copper.org/applications/electrical/busbar/bus_table1.html
- **Source: Aluminum Association https://www.aluminum.org/sites/default/files/aecd13.pdf
Note: Ratings depend upon configuration, air flow, ambient temp, etc. The values depicted are an approximation. Controlled testing is always required to validate.
Other considerations:
- Forming the busbar (aluminum has a tendacy to crack with very tight radius)
- Electroplating the busbar (white rust on aluminum, oxidation is an issue with aluminum)
- Configuration of the busbar (vertical or horizontal configuration)
Conductive aluminum busbar size reference table
Aluminum Busbar - Sharp Corners (Standard)
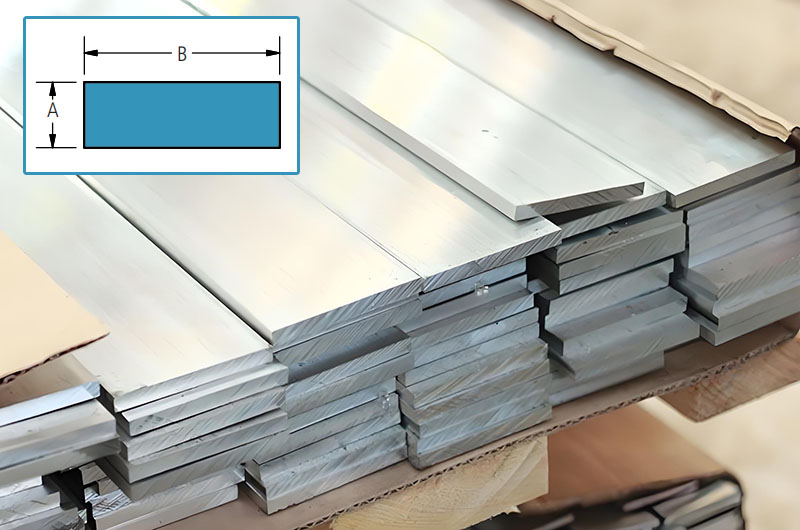

| Thickness A (in) | Width B (in) | Estimated Weight per lb/ft |
| 1/8 | 0.375 | 0.055 |
| 1/8 | 0.500 | 0.074 |
| 1/8 | 0.625 | 0.090 |
| 1/8 | 0.750 | 0.110 |
| 1/8 | 0.875 | 0.127 |
| 1/8 | 1.000 | 0.149 |
| 1/8 | 1.250 | 0.184 |
| 1/8 | 2.000 | 0.299 |
| 1/8 | 2.500 | 0.371 |
| 1/8 | 4.000 | 0.599 |
| 3/16 | 0.375 | 0.084 |
| 3/16 | 0.500 | 0.112 |
| 3/16 | 0.625 | 0.140 |
| 3/16 | 0.750 | 0.168 |
| 3/16 | 0.875 | 0.187 |
| 3/16 | 1.000 | 0.222 |
| 3/16 | 2.000 | 0.442 |
| 1/4 | 0.500 | 0.149 |
| 1/4 | 0.750 | 0.209 |
| 1/4 | 1.000 | 0.284 |
| 1/4 | 1.250 | 0.359 |
| 1/4 | 1.500 | 0.434 |
| 1/4 | 2.000 | 0.584 |
| 1/4 | 2.500 | 0.734 |
| 1/4 | 3.000 | 0.884 |
| 1/4 | 3.250 | 0.959 |
| 1/4 | 4.000 | 1.184 |
| 1/4 | 4.500 | 1.334 |
| 1/4 | 5.000 | 1.484 |
| 1/4 | 6.000 | 1.784 |
| 1/4 | 7.000 | 2.084 |
| 1/4 | 8.000 | 2.384 |
| 3/8 | 0.625 | 0.277 |
| 3/8 | 1.25 | 0.527 |
| 3/8 | 2 | 0.864 |
| 3/8 | 2.5 | 1.120 |
| 3/8 | 3 | 1.134 |
| 3/8 | 4 | 1.764 |
| 3/8 | 5 | 2.214 |
| 3/8 | 6 | 2.664 |
| 3/8 | 8 | 3.596 |
| 1/2 | 0.75 | 0.385 |
| 1/2 | 1.5 | 0.896 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 1.196 |
| 1/2 | 3 | 1.796 |
| 1/2 | 4 | 2.396 |
| 1/2 | 5 | 2.996 |
| 1/2 | 6 | 3.596 |
| 1/2 | 8 | 4.796 |
| 1/2 | 10 | 5.996 |
| 3/4 | 1 | 0.884 |
| 3/4 | 4 | 3.455 |
| 3/4 | 5 | 4.495 |
| 1 | 1.25 | 1.498 |
| 1 | 8 | 9.535 |
| 1 | 10 | 11.996 |
| 1 | 12 | 14.364 |
Rounded Corners Aluminum Busbar
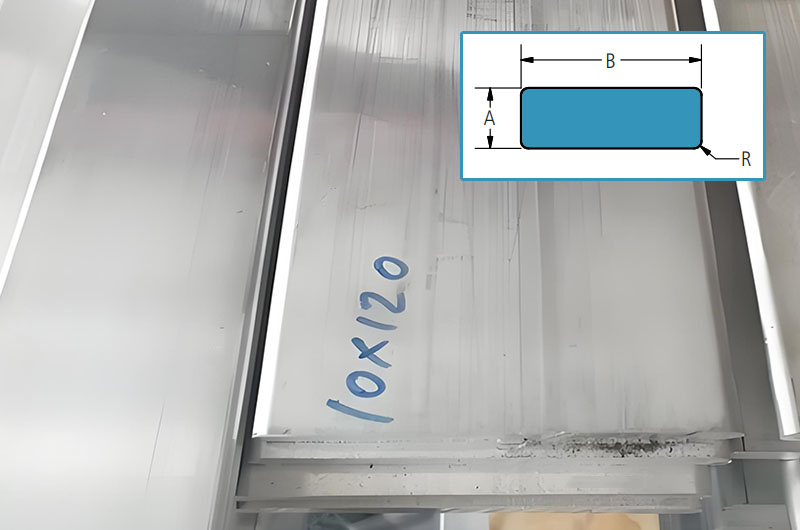
| Thickness A (in) | Width B (in) | Radius R (in) | Estimated Weight per lb/ft |
| 1/8 | 0.375 | 0.031 | 0.055 |
| 1/8 | 0.5 | 0.016 | 0.074 |
| 1/8 | 0.5 | 0.031 | 0.074 |
| 1/8 | 0.625 | 0.062 | 0.09 |
| 1/8 | 0.75 | 0.031 | 0.11 |
| 1/8 | 0.875 | 0.062 | 0.127 |
| 1/8 | 1 | 0.031 | 0.149 |
| 1/8 | 1.25 | 0.062 | 0.184 |
| 1/8 | 2 | 0.031 | 0.299 |
| 1/8 | 2.5 | 0.031 | 0.371 |
| 1/8 | 4 | 0.031 | 0.599 |
| 3/16 | 0.375 | 0.031 | 0.084 |
| 3/16 | 0.5 | 0.031 | 0.112 |
| 3/16 | 0.625 | 0.031 | 0.14 |
| 3/16 | 0.75 | 0.016 | 0.169 |
| 3/16 | 0.75 | 0.031 | 0.168 |
| 3/16 | 0.875 | 0.094 | 0.187 |
| 3/16 | 1 | 0.062 | 0.222 |
| 3/16 | 2 | 0.094 | 0.442 |
| 1/4 | 0.5 | 0.031 | 0.149 |
| 1/4 | 0.75 | 0.125 | 0.209 |
| 1/4 | 1 | 0.125 | 0.284 |
| 1/4 | 1.25 | 0.125 | 0.359 |
| 1/4 | 1.5 | 0.125 | 0.434 |
| 1/4 | 2 | 0.125 | 0.584 |
| 1/4 | 2.5 | 0.125 | 0.734 |
| 1/4 | 3 | 0.125 | 0.884 |
| 1/4 | 3.25 | 0.125 | 0.959 |
| 1/4 | 4 | 0.125 | 1.184 |
| 1/4 | 4.5 | 0.125 | 1.334 |
| 1/4 | 5 | 0.125 | 1.484 |
| 1/4 | 6 | 0.125 | 1.784 |
| 1/4 | 7 | 0.125 | 2.084 |
| 1/4 | 8 | 0.125 | 2.384 |
| 3/8 | 0.625 | 0.062 | 0.277 |
| 3/8 | 1.25 | 0.188 | 0.527 |
| 3/8 | 2 | 0.062 | 0.895 |
| 3/8 | 2 | 0.187 | 0.864 |
| 3/8 | 2.5 | 0.062 | 1.12 |
| 3/8 | 3 | 0.187 | 1.314 |
| 3/8 | 5 | 0.187 | 2.214 |
| 3/8 | 4 | 0.187 | 1.764 |
| 3/8 | 6 | 0.187 | 2.664 |
| 3/8 | 8 | 0.062 | 3.596 |
| 1/2 | 0.75 | 0.250 | 0.385 |
| 1/2 | 1.5 | 0.062 | 0.896 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 0.062 | 1.196 |
| 1/2 | 3 | 0.062 | 1.796 |
| 1/2 | 4 | 0.062 | 2.396 |
| 1/2 | 5 | 0.062 | 2.996 |
| 1/2 | 6 | 0.062 | 3.596 |
| 1/2 | 8 | 0.062 | 4.796 |
| 1/2 | 10 | 0.062 | 5.996 |
| 3/4 | 1 | 0.125 | 0.884 |
| 3/4 | 4 | 0.375 | 3.455 |
| 3/4 | 5 | 0.062 | 4.495 |
| 1/1 | 1.25 | 0.031 | 1.498 |
| 1/1 | 8 | 0.25 | 9.535 |
| 1/1 | 10 | 0.062 | 11.996 |
| 1/1 | 12 | 0.188 | 14.364 |
Aluminum Busbar Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Process: Extrusion of complex shapes, precision cutting, drilling, and surface treatment.
- Quality control checks: Dimensional accuracy, conductivity testing, and coating adhesion.
Aluminum Busbar Environmental Considerations
Aluminum busbars provide a cost-effective and lightweight solution for modern electrical systems, striking a balance between performance and practical design considerations. Their versatility makes them an essential component in industries that prioritize efficiency and sustainability.
- Outdoor use: Anodized or coated layers with UV/salt spray resistance.
- Sustainability: Fully recyclable, reducing the environmental impact over the product’s lifecycle.
Common Issues and Solutions for Aluminum Busbars
- Oxidation: Use of coatings or anti-oxidation paste.
- Vibration loosening: Use of thread-locking adhesives or anti-vibration hardware.
- Creep: Design joints to accommodate material flow under pressure.
Installation and Maintenance
- Connections: Use of anti-oxidation compounds, stainless steel hardware, or bimetallic connectors to prevent electrochemical corrosion.
- Thermal management: Leave expansion gaps; use torque specifications and lock washers to secure bolted connections.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection for corrosion, joint tightening, and surface cleaning. Use of Belleville washers or re-tightening schedules to address loosening caused by creep.
Considerations
While aluminum busbars offer many advantages, it is important to ensure proper installation and maintenance to prevent issues such as oxidation at connection points, which can increase resistance and reduce efficiency. Regular inspections and appropriate protective measures help maintain optimal performance.
Aluminum busbars are crucial components in electrical systems, featuring high conductivity, lightweight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Aluminum Busbar Purchasing Guide
- Conductivity: Aluminum’s conductivity is about 61% of copper’s, but it is lighter and more cost-effective, making it suitable for most power transmission applications.
- Current carrying capacity: The current carrying capacity of aluminum busbars varies depending on their size and shape.
- Size: The size of aluminum busbars should be determined based on specific application requirements to ensure they meet current carrying capacity and installation space needs.
- Alloy selection: Different aluminum alloys have varying mechanical properties and conductivity; choosing the right alloy is crucial to meet specific application needs.
- Shape: Aluminum busbars can be flat, angled, or custom-extruded profiles, with the choice of shape depending on installation space and electrical connection requirements.
- Surface treatment: Surface treatments such as polishing, anodizing, or plating (tin/silver) can reduce oxidation, improve contact resistance, and extend the lifespan of the busbar.
| Factor | Details |
| Electrical Conductivity | Aluminum has about 61% the conductivity of copper. This means aluminum busbars need to be larger in cross-section for the same current-carrying capacity. |
| Current-Carrying Capacity | The ampacity depends on dimensions, material, and temperature. An approximate formula: I = 0.8 × Width (mm) × Thickness (mm) is used for sizing. |
| Dimensions | The size of the busbar must match the required current-carrying capacity and minimize resistance. Custom sizes may be required for specific applications. |
| Alloy Selection | Common alloys for busbars: 6061-T6 (good mechanical properties), 6063-T52 (excellent corrosion resistance), 1350 (high conductivity). Alloy choice affects strength and conductivity. |
| Shape | Busbars are available in flat, angled, or custom extruded profiles to meet specific installation needs. Custom shapes can optimize space and performance. |
| Surface Treatment | Various treatments like polishing (reduces resistance), anodizing (corrosion resistance), or electroplating (tin/silver, improves conductivity and reduces oxidation). |
| Mechanical Strength and Durability | Busbars must resist mechanical stresses, including thermal expansion. Alloy and temper affect strength and flexibility. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum’s natural oxide layer provides basic corrosion resistance. Anodizing further improves resistance, especially for harsh environments. |
| Thermal Expansion | Aluminum has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to copper. This needs to be accounted for in design to avoid issues with temperature changes. |
| Weight | Aluminum is lighter than copper, making installation easier and reducing structural support requirements. This can lead to cost savings. |
| Cost | Aluminum is more cost-effective than copper, making it a good option for large-scale applications where budget is a concern. |
| Environmental Impact | Aluminum is highly recyclable and uses less energy in recycling than its production, making it an environmentally friendly choice. |
By carefully evaluating these characteristics, customers can select the aluminum busbar that best meets their specific requirements, balancing performance, cost, and environmental factors.












